-
Research on Spatially-aware LLM Agents
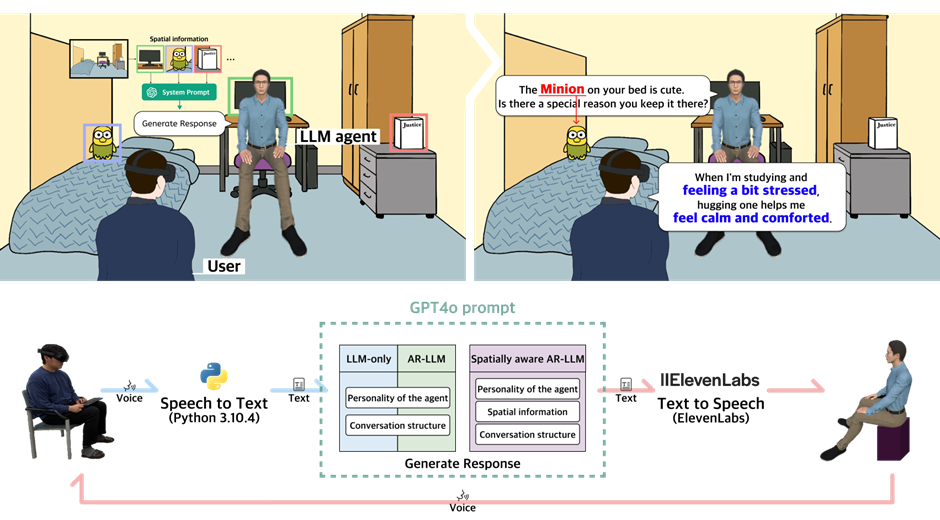
Large language models (LLMs) are evolving into agents capable of social interaction. This study explored how users interact with spatially aware LLM agents that can understand and reference the user's real-world environment. Participants had counseling conversations with three types of LLM agents: one with no spatial awareness, one in an AR setting, and one that could actually recognize and refer to the user's space. Results showed that when the LLM agent understood the space, users felt more connected, trusted the agent more, and shared more personal thoughts. This shows that adding spatial awareness to LLMs can make them more effective and emotionally engaged, especially in areas like counseling, education, and healthcare.
-
For more details, see “When LLMs Recognize Your Space: Research on Experiences with Spatially Aware LLM Agents (IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics, 2025; Presented ISMAR 2025, *Best Paper Award*).”
-
Research on Inter-Brain Synchronies in Remote AR Interactions
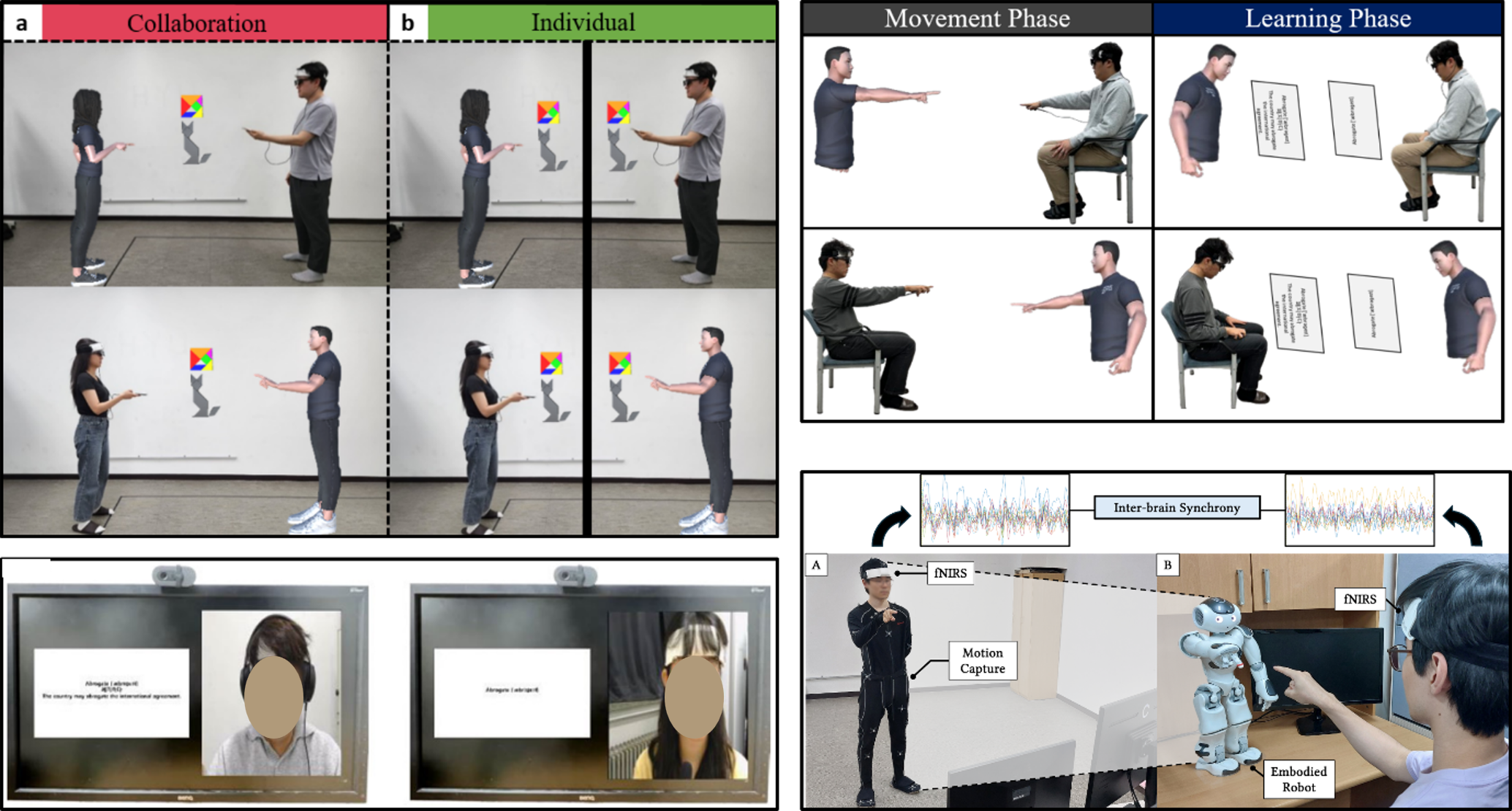
Inter-brain Synchrony (IBS) has emerged as an objective neurophysiological indicator that reflects the quality of interaction. However, previous studies have been largely confined to typical face-to-face contexts. To address this gap, we conducted a series of four studies examining IBS across three types of remote interaction modalities: webcam-based, remote AR, and robot-mediated interactions. Through these studies, we contributed to understanding interpersonal synchrony mechanisms in remote interactions, confirmed the potential of IBS as a neural index for evaluating remote social interaction and educational quality, and demonstrated the positive effects of behavioral synchrony.
For more details, see “Can People’s Brains Synchronize during Remote AR Collaboration? (IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics, 2025)”, and “Inter Brain Synchrony in Remote AR Education: Can Warming up Activities Positively Impact Educational Quality? (ISMAR, 2024).”
-
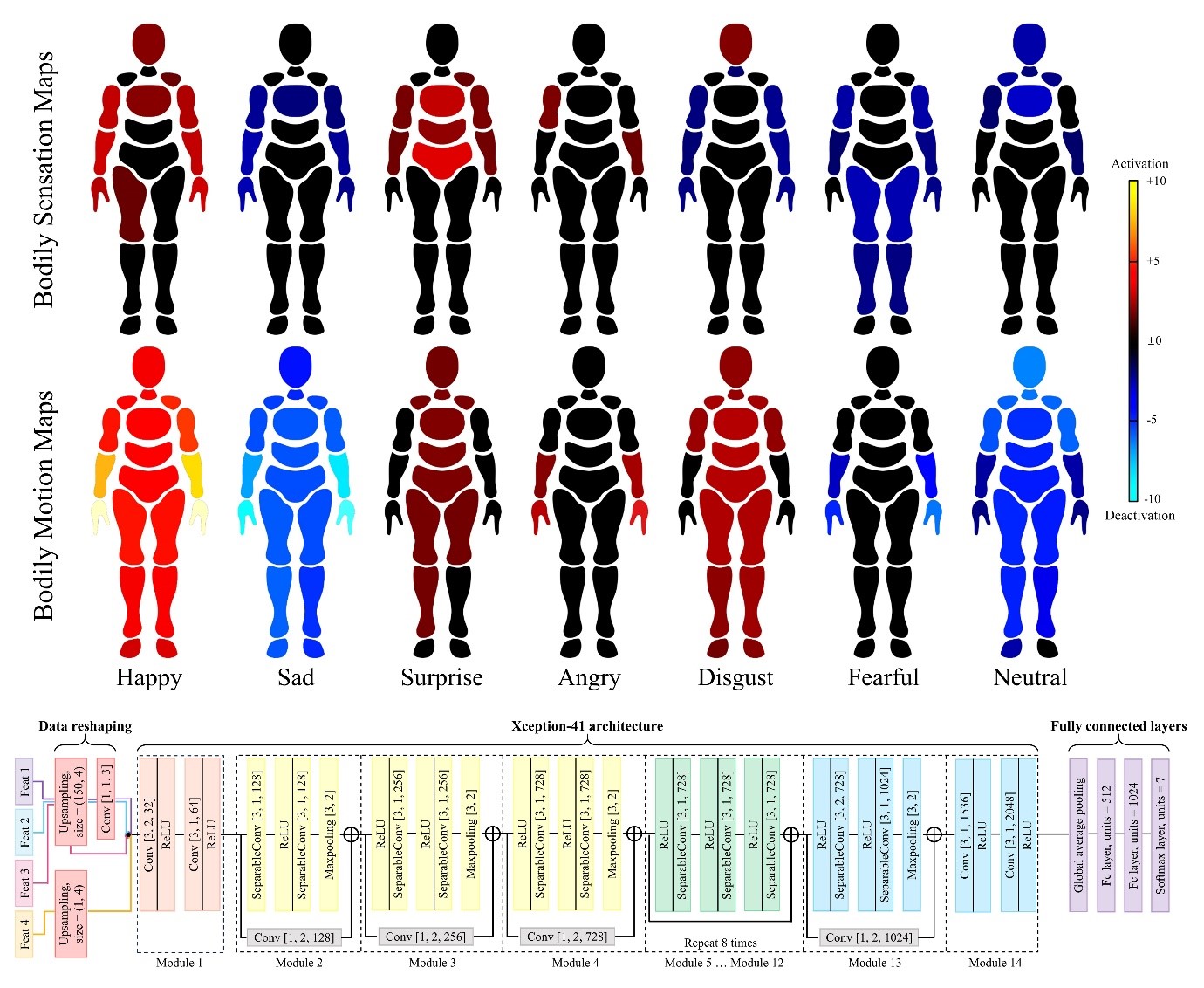
Research on Emotion Recognition using Body Motion
Emotion can be shown through various modalities (facial expression, vocal tone, and body motion). Among these modalities, emotional expression through body has been underestimated. This study investigated and compared how emotions are revealed through bodily sensations and body movement information. We proposed a novel visualization method for addressing body joint activation and deactivation associated with different emotional status using motion capture data. We have also proposed a CNN-based automatic emotion recognition system which outperforms humans’ emotion recognition ability. Our research would shed a light on emotion recognition using body motion, which is beneficial that it contains less personal information compared to other emotion modalities and can be used with low-resolution systems such as CCTV.
-
For more details, see “Bodily Sensation Map vs. Bodily Motion Map: Visualizing and Analyzing Emotional Body Motions (IEEE Transactions on Affective Computing, 2024).”
Research on Individualized Rendering for Virtual Reality
Foveated rendering (FR) technology is designed to improve the efficiency of graphical rendering processes. In rendering, individualized approaches can help to balance users’ experiences of visual quality and saving computational resource. However, previous studies have not rigorously examined it related with the FR techniques. To address this issue, we developed an individualized FR (IFR) method using different central vision sizes and peripheral vision resolutions across individuals in virtual reality. Through this technique, users’ quality of virtual experience is not hindered, and computational power can be saved simultaneously. Although lower-bound adjustments may be required for some users, our overall results suggest that IFR is a malleable technology for enhancing rendering efficiency in virtual reality. This study is published in Virtual Reality journal (Springer, IF: 4.2) in 2024.
For more details, see “Individualized foveated rendering with eye-tracking head-mounted display (Virtual Reality, 2024).”
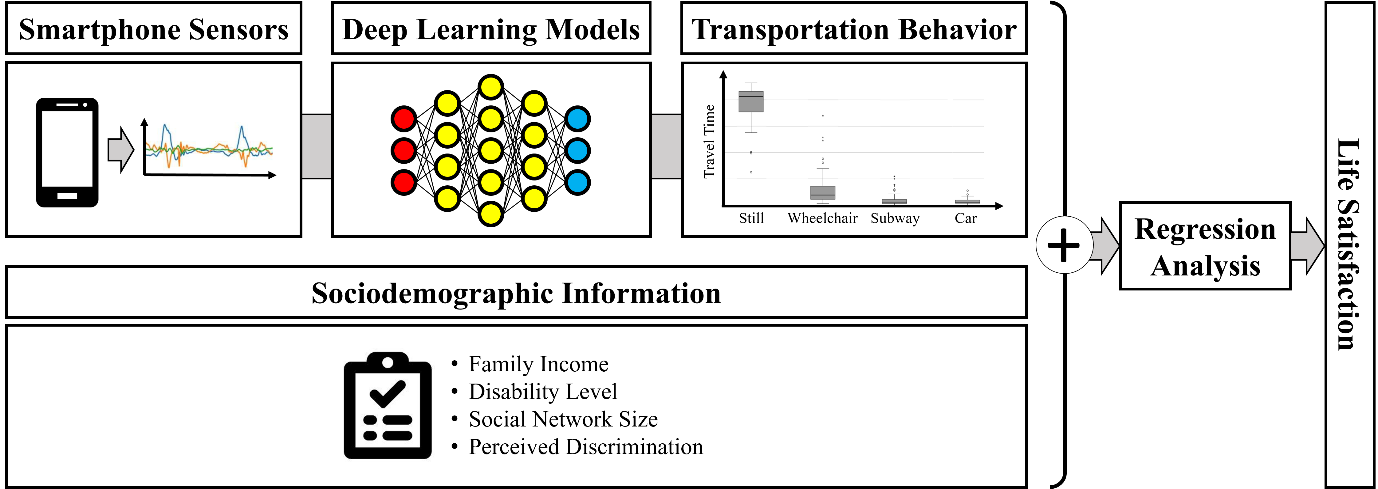
Research on Human Behavior Analysis using Smartphone Sensor Data
Understanding human behavior through computing technology is a significant aspect of human-computer interaction. Sensor data from smartphones and smartwatches, combined with deep learning techniques, are widely employed to recognize human behaviors. Our research leverages sensor data from these devices to explore the travel behaviors of people with disabilities. Furthermore, we demonstrate how insights derived from sensing and deep learning technologies can contribute to analyzing social scientific phenomena.
For more details, see “User and Period Independent Transportation Mode Detection for Wheelchair Users (IEEE Access, 2023),” “User-Independent Motion and Location Analysis for Sussex-Huawei Locomotion Data (UbiComp/ISWC '23 Adjunct, 2023),” “Transportation Mode Detection Technology to Predict Wheelchair Users’ Life Satisfaction in Seoul, South Korea (IMWUT, 2024)”
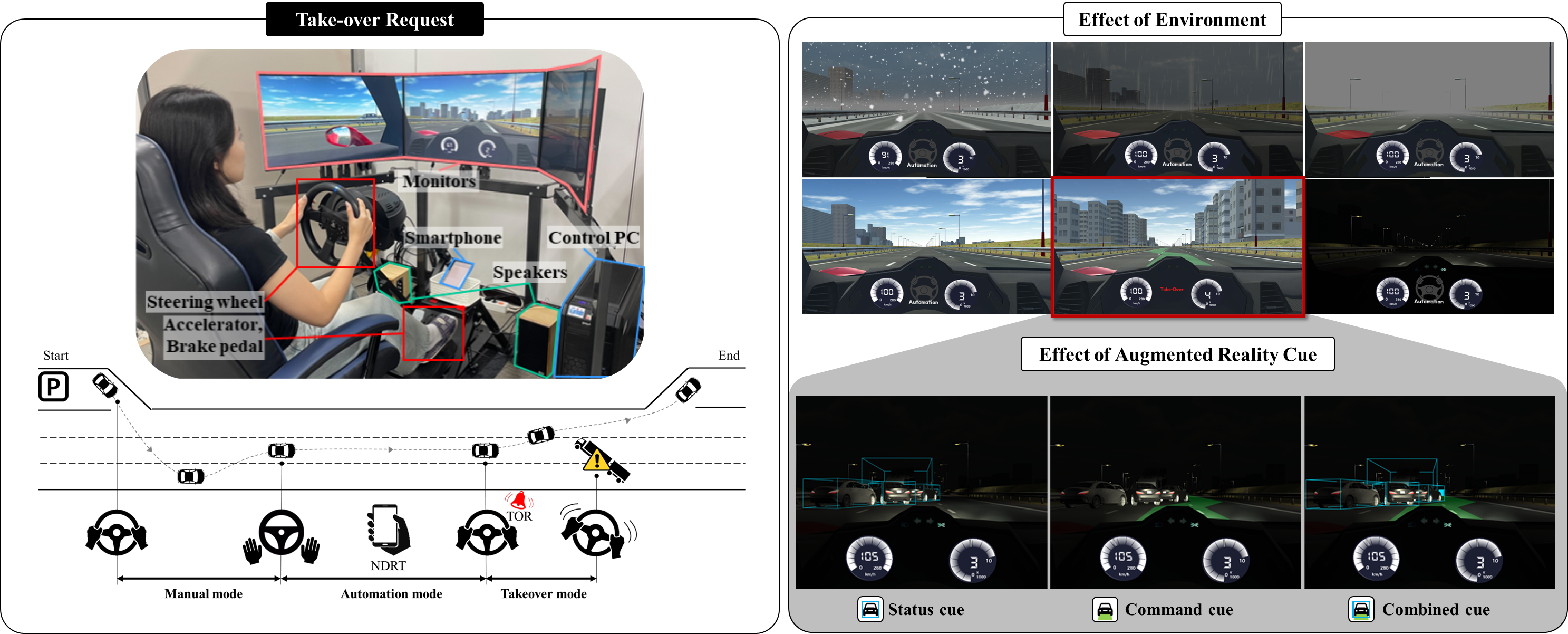
Research on Human-Vehicle Interaction
Our research primarily focused on human-vehicle interactions in Level 3 autonomous vehicles, emphasizing the investigation of the impact of environmental factors and Augmented Reality (AR) cue stimuli on driver performance during Takeover Requests (TORs). Our findings showed that while environmental factors influenced TOR performance, AR cues could effectively mitigate these effects. We also discovered that the effectiveness of different types of AR signals, such as command and status cues, varied depending on the environment. Command cues generally enhanced driving performance, whereas status cues were particularly effective at night. This indicates that AR designs in autonomous vehicles should be customized to specific environmental conditions to ensure optimal driver-vehicle collaboration.
For more details, see “Responses to Take-Over Request in Autonomous Vehicles: Effects of Environmental Conditions and Cues, (IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2022),” “Interaction between AR Cue Types and Environmental Conditions in Autonomous Vehicles (ISMAR, 2023).”
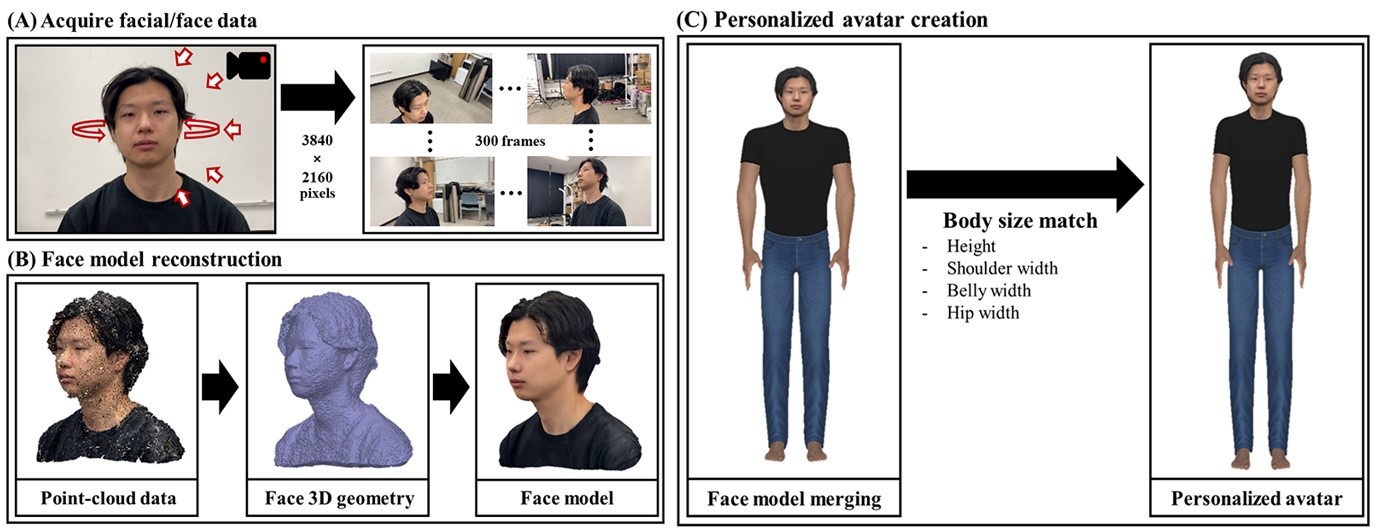
Research on Personalized Avatar
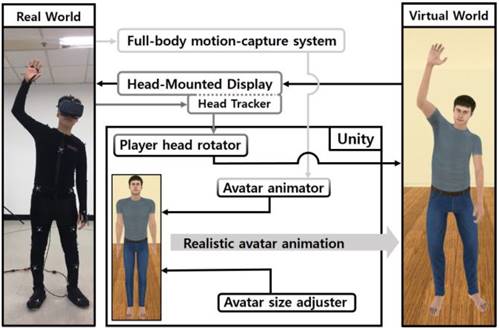
Through advances in technologies, we can make personalized avatar which is a virtual avatar that resembles user’s appearance. Current state-of-the-art full-body 3D scanner requires multiple high-resolution cameras (about 130~140 cameras) and dedicated space. Which results in low accessibility for normal users. We proposed a method for facilitating personalized avatar using single smartphone. Our research would benefit various applications for easy usage on personalized avatar which results in high-quality virtual experiences.
For more details, see “Impact of Personalized Avatars and Motion Synchrony on Embodiment and Users’ Subjective Experience: Empirical Study (JMIR Serious Games, 2022).”
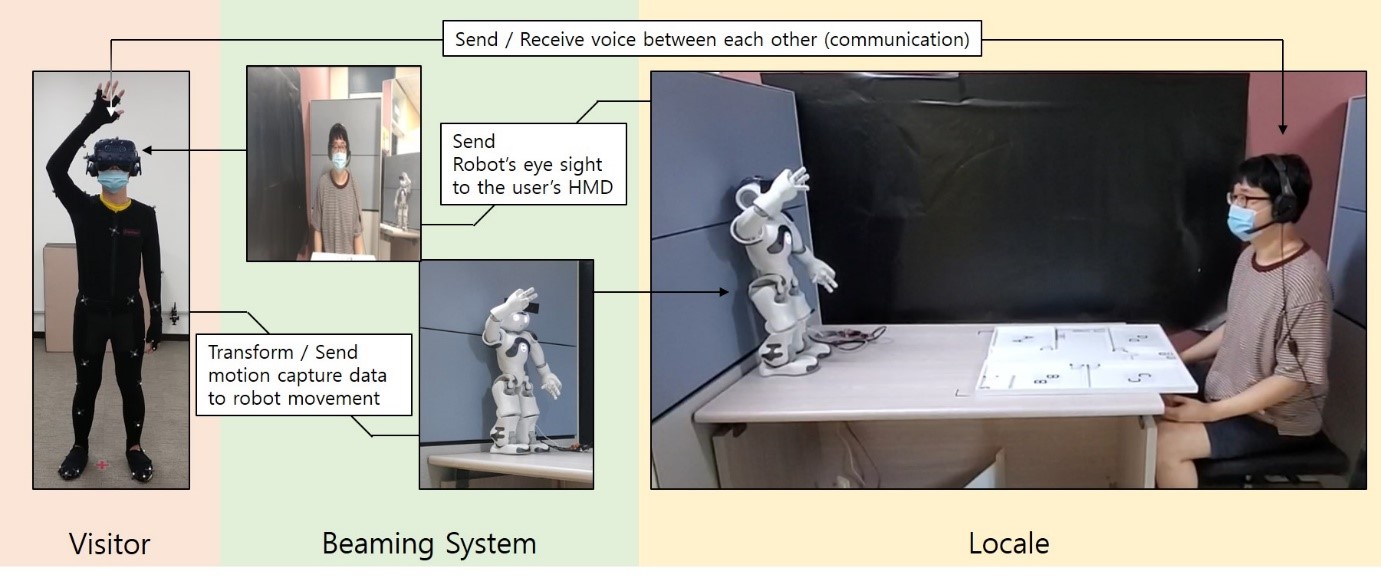
- Research on Body Ownership Illusion Toward Humanoid Robot
Through advances in recent technologies, we can make users to feel an illusory feeling of body ownership toward humanoid robot at the remote places. Such asymmetric tele-embodiment system has the power to elicit presence (toward remote distance a.k.a. locale), social interaction, and emotional change between visitor and locale. Our research would be a game changer for the tele-communication in the post-corona era (e.g. general purpose telecommunication, untact interview, untact psychological counsel). Researches may extend to verify the actual therapeutic effect under current circumstances.
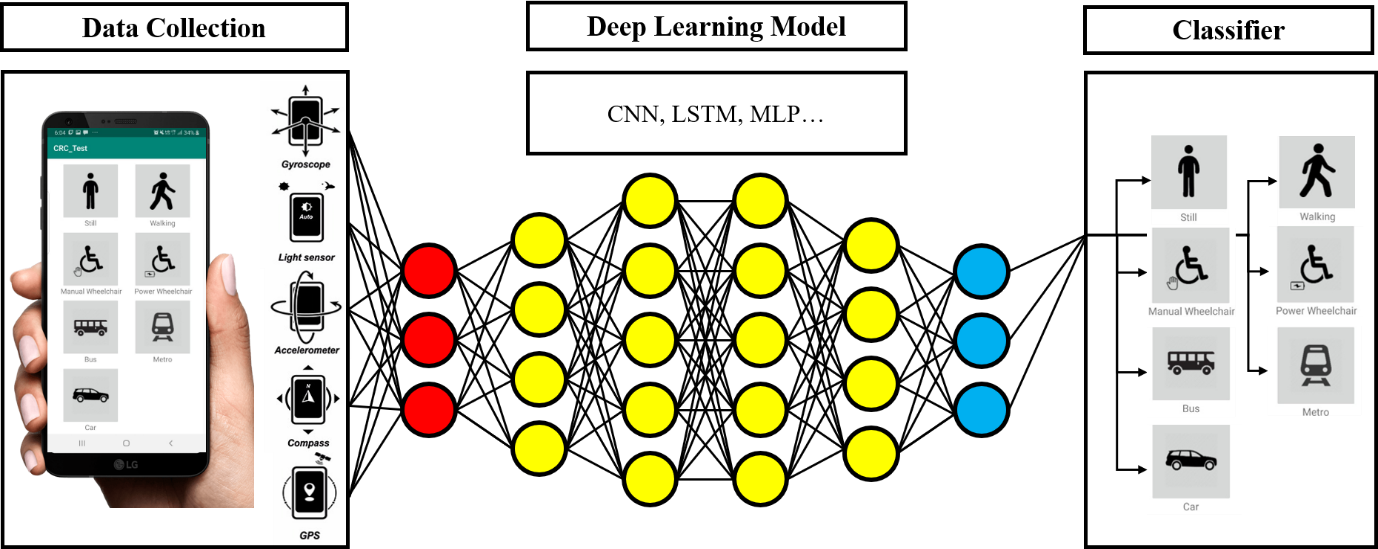
Research on Human-AI interaction
With development of deep learning technologies, we are conducting research on Human-AI. In our study, we are collecting and analyzing mobility data for people with handicaps. Our result suggest that our deep learning model had high accuracy for detecting transportation modes for people with handicaps. Based on the current study, we will suggest better Human-AI interaction to help people with handicaps.
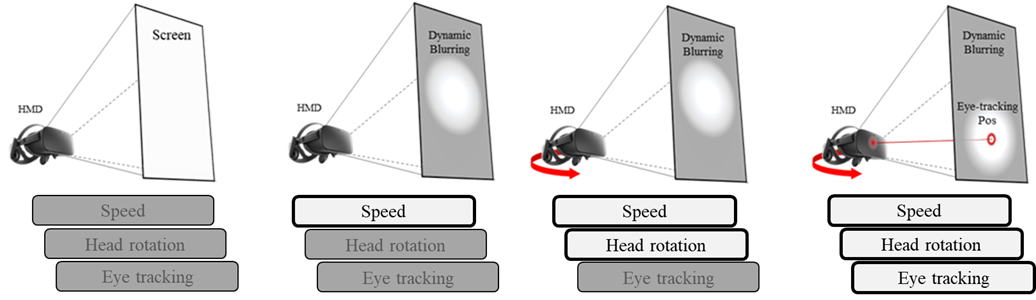
Research on VR Sickness
Although the virtual reality (VR) market is extremely large, the VR sickness is one of the big problems. The VR sickness had a symptom similar with motion sickness experienced when experiencing VR, including headache, nausea, and dizziness., In one of our study, we proposed a method to dynamic blurring field of view (FOV) restrictor based on the relationship between FOV and VR sickness. We studied the effect of several factors on VR sickness when applied as dynamic parameters. As a result, dynamic blurring FOV restrictor had the effect of reducing VR sickness, and it had the best performance when we apply certain level of appropriate human factors.
- Research on Full-Body Ownership Illusion
Recent advances in technology have allowed users to experience an illusory feeling of full body ownership of a virtual avatar. Such virtual embodiment has the power to elicit perceptual, behavioral, cognitive, and emotional changes related to oneself. Our research would be an important foundation for new collaborations with virtual avatars or humanoid robots. For example, collaborative therapeutic techniques and scenarios with other artificial surrogates would be considered based on the paradigm of a virtually embodied self. Researches may extend interaction domains from the individuals to the virtual avatars in an artificial world or tele-operations of humanoid robots in real world.
- Research on Human-Robot Interaction
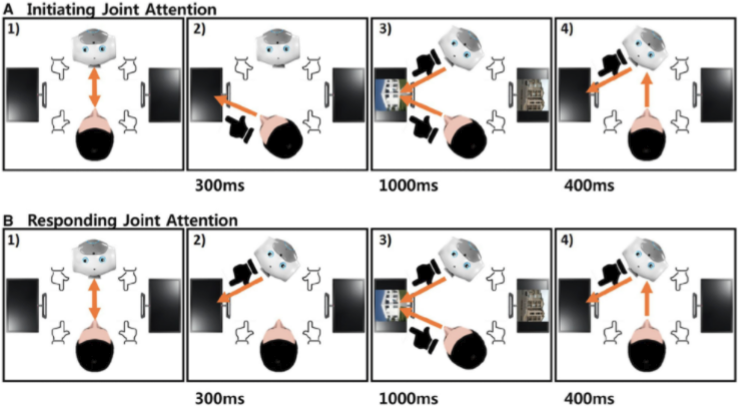
Recent Studies on human-robot interactions have suggested that humanoid robots have considerable potential in social cognition research. In the current study, we considerd two types of social interaction tasks (initiating and responding inout attenntion tasks) and two types of interaction partners (robot and human partners). The results of study suggested that participants who interacted with a humanoid robots in social cognition studies and future research questions on human-robot interactions.
Recent Studies on human-robot interactions have suggested that humanoid robots have considerable potential in social cognition research. In the current study, we considerd two types of social interaction tasks (initiating and responding inout attenntion tasks) and two types of interaction partners (robot and human partners). The results of study suggested that participants who interacted with a humanoid robots in social cognition studies and future research questions on human-robot interactions.
- Research on Human Field of Regard and Field of View
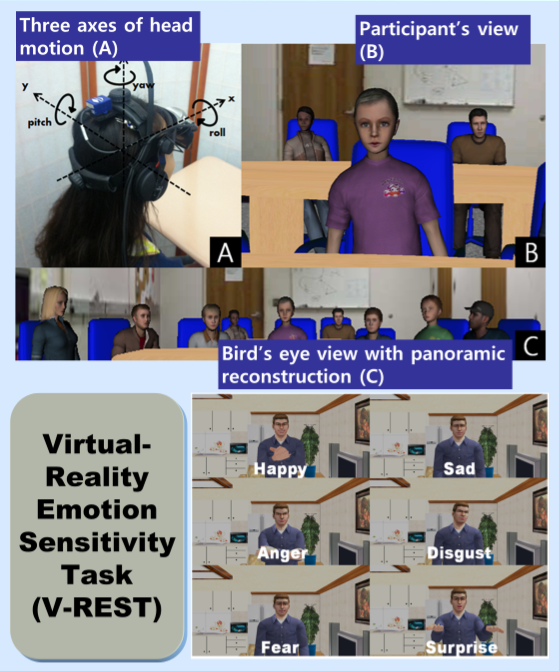
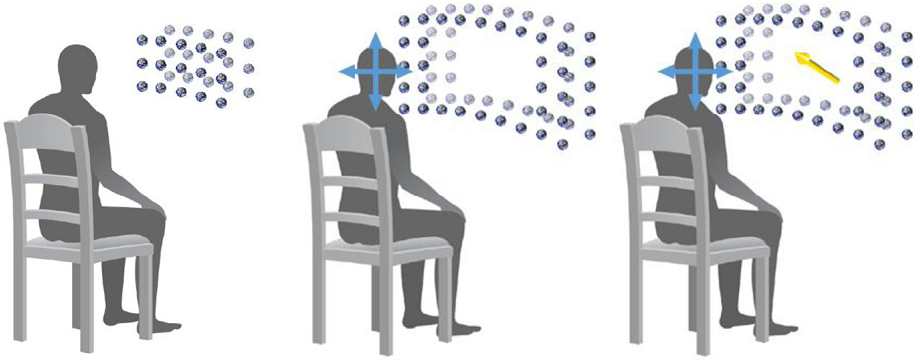
Human field of regard (FOR) is an important concept that should be considered along with field of view (FOV) for people with/without handicaps, but previous studies have neglected this aspect of human perception. In the current study, we suggest and test a new virtual reality (VR) software with which to evaluate individual’s detection abilities in the human FOR. We suggested a new virtual reality (VR) evaluation technique and measured the human searching pattern in the FOR condition. We found a unique left-side attention bias in the FOR condition, and discussed implication of these results and potential attention bias factors. We believe this work is an important foundation for interactive 3D UI design, and we hope it will help people who have FOR handicaps.
- Effect of Human-Computer Interaction Platforms (e.g., virtual reality platform)
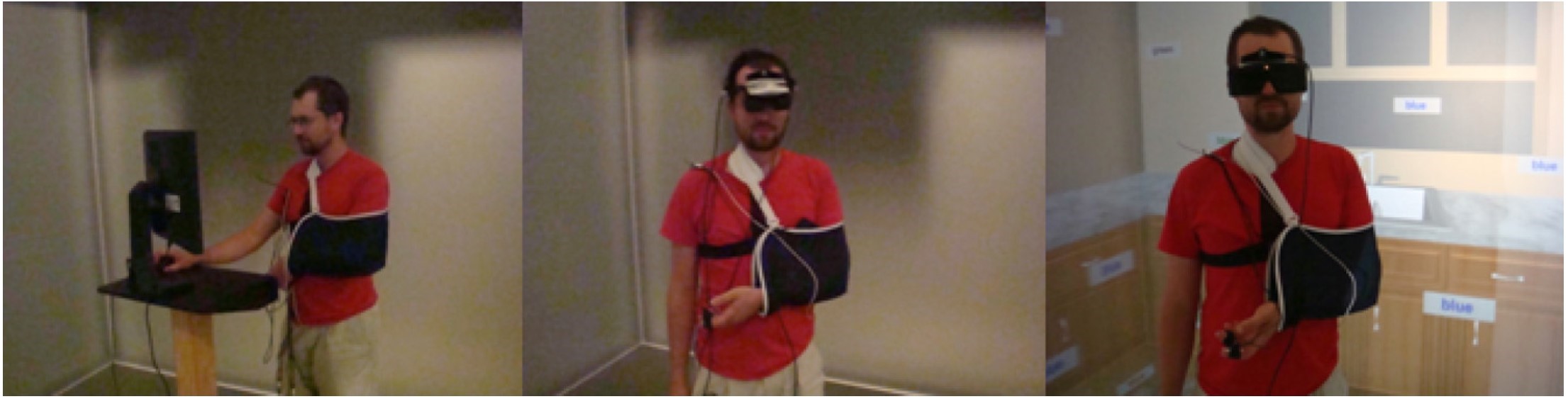
The goal of this project is to investigate the effects of different human-computer interaction platforms (i.e., virtual environment technologies: desktop, head mounted display, or fully immersive platforms) on human’s cognition, emotion, and behavior. Our findings suggest that different VE systems may be appropriate for different scientific purposes when studying stress reactivity using emotionally evocative tasks.
-
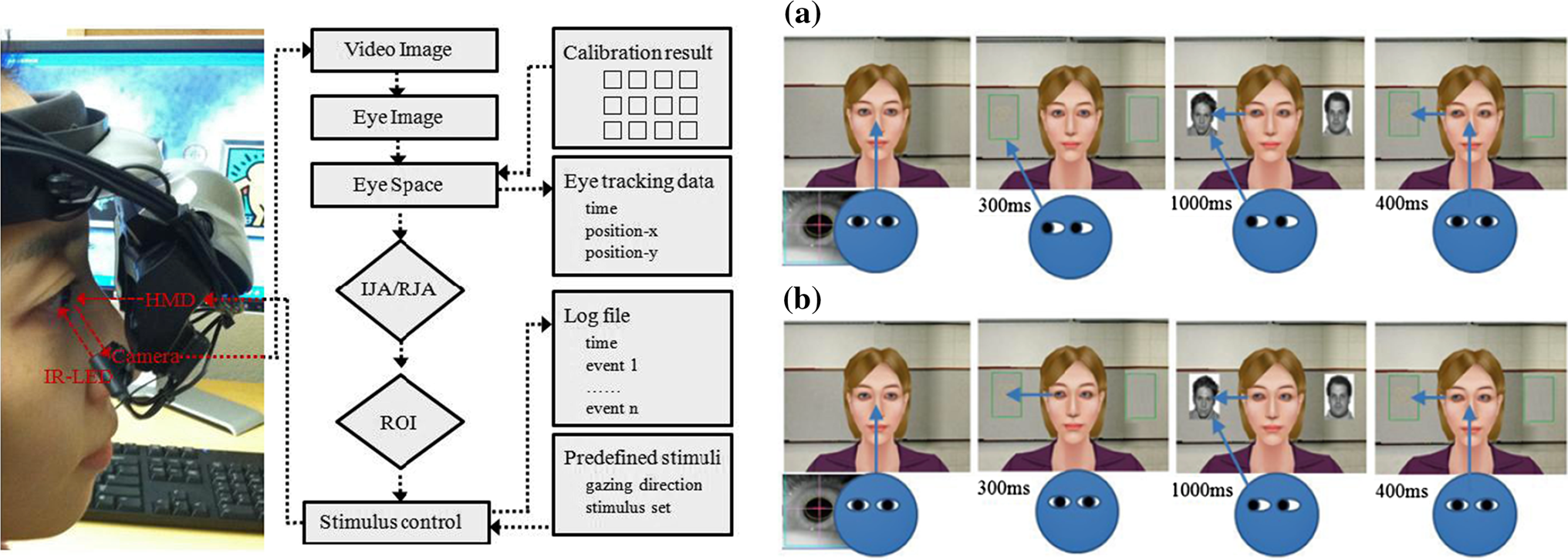
Human-Computer Interaction (HCI) Technology for People with Autism Spectrum Disorders
Research on joint attention has played a significant role in defining critical features of the social-cognitive development of children with Autism Spectrum Disorders (ASD). We developed virtual reality paradigm that integrates eye-tracking and virtual avatar technology to study about ASD.
-
Computer-based Behavioral Measure for People with Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder
Easy to administer behavioral measures are needed to improve the assessment of this hallmark feature of psychiatry disorder. We recently developed a new computer-based behavioral assessment of obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD). Our new behavioral measure offers a novel, objective, and ecologically valid measure of checking behaviors in a sample of adults with OCD.
-
-

- Virtual Reality-Social Skill Training (VR-SST) for People with Schizophrenia
Impairment in social skills is one of the few criteria that all individuals diagnosed with schizophrenia must meet. Successful social skills require the coordination of many abilities, including social perception, which involves the decoding and interpretation of social cues from others. We developed virtual reality social skill training (VR-SST).